A baseball agent can make anywhere from a few hundred thousand dollars to tens of millions of dollars annually. The baseball agent salary is largely tied to the success of their clients and the commission they earn on player contracts and endorsements. This article will delve into the financial landscape of baseball agents, exploring MLB agent earnings, commission for baseball agents, and the overall sports agent income.
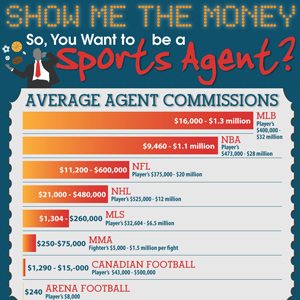
Image Source: www.sportsmanagementdegreehub.com
Deciphering Sports Agent Compensation
Sports agents, particularly in the high-stakes world of Major League Baseball (MLB), operate on a commission-based system. This means their earnings are directly proportional to the success and earning potential of the players they represent. While there’s no fixed annual baseball agent salary in the traditional sense, their income can be substantial, fueled by signing bonuses, annual salaries negotiated, and lucrative endorsement deals.
How Agents Get Paid: The Commission Structure
The primary way baseball agents get paid is through baseball player representation fees, commonly referred to as commission. The standard commission rate for player contracts in MLB is typically 5% of the total value of the contract. This commission is paid out to the agent as the player receives their salary installments.
Beyond contract negotiations, agents also earn commissions on endorsement deals, which can range from 10% to 20% of the deal’s value. These supplementary income streams are crucial for many agents, especially those representing high-profile players with significant marketability.
Factors Influencing MLB Agent Earnings
Several key factors dictate how much a baseball agent makes:
- Client Roster Quality: The caliber and earning potential of the players an agent represents are paramount. An agent with several star players earning multi-million dollar contracts will naturally generate higher MLB agent earnings than an agent with a roster of minor league or role players.
- Contract Negotiation Prowess: An agent’s ability to negotiate favorable contract terms, including higher salaries, longer guarantees, and valuable clauses (like no-trade clauses or opt-out options), directly impacts the overall value of the contracts they secure, thus increasing their commission.
- Endorsement Deal Success: Securing lucrative endorsement deals for clients can significantly boost an agent’s income. This requires strong marketing skills and an understanding of a player’s brand potential.
- Agency Size and Revenue: Larger sports agencies often have more resources, better connections, and a broader client base, which can lead to higher overall sports agency revenue and, consequently, better earnings for their agents.
- Years of Experience and Reputation: Experienced agents with a proven track record of success and a strong reputation within the industry tend to attract higher-tier clients, leading to greater earning potential.
- Market Demand: The demand for an agent’s services, influenced by the player’s draft position, potential, and team needs, also plays a role.
The Typical Baseball Agent Salary vs. Top Earners
While it’s difficult to pinpoint an exact average salary for sports agent in baseball due to the commission structure, we can analyze the potential income based on contract values and commission rates.
Commission for Baseball Agents: A Deeper Dive
Let’s break down how commission for baseball agents works with an example:
Imagine an agent represents a player who signs a 5-year contract worth $100 million. At a 5% commission rate, the agent would earn:
$100,000,000 (Contract Value) * 0.05 (Commission Rate) = $5,000,000
This $5 million would be earned over the life of the contract, paid out as the player receives their salary. If the player also secures a 3-year, $5 million endorsement deal, the agent might earn:
$5,000,000 (Endorsement Value) * 0.15 (Average Endorsement Commission) = $750,000
In this scenario, the agent earns a total of $5.75 million from this one client’s contract and endorsements. However, agents typically represent multiple players, and not all contracts are this lucrative.
Estimating Sports Agent Income
To get a broader picture, let’s consider the sports agent income range:
- Rookie Agents: Agents just starting out, often representing minor league players or those on shorter, less lucrative contracts, might earn anywhere from $50,000 to $150,000 in their initial years. Their earnings are heavily dependent on securing their first few clients and negotiating modest contracts.
- Mid-Level Agents: Agents with a few years of experience and a solid roster of players on MLB rosters could see their earnings range from $200,000 to $1 million annually. This often involves negotiating contracts in the low to mid-seven figures and securing some endorsement opportunities.
- Top-Tier Agents: Elite agents representing All-Stars and superstars can command earnings well into the millions, often exceeding $5 million to $10 million or more annually. These agents are masters of contract negotiation commission, securing massive deals and top-tier endorsement packages for their clients. Their baseball agent salary is a reflection of their ability to maximize their clients’ earning potential.
The Business of Sports Agency Revenue
Sports agencies are businesses, and their overall sports agency revenue is derived from the collective commissions earned by all their agents. Larger agencies with more agents and a higher concentration of top clients generate significant revenue.
How Agencies Operate
Sports agencies offer a range of services to their clients, including:
- Contract Negotiation: Securing the best possible playing contracts.
- Marketing and Endorsement Deals: Finding and negotiating lucrative off-field opportunities.
- Financial Planning: Connecting players with financial advisors.
- Career Management: Guiding players through their careers and post-playing opportunities.
- Brand Building: Helping players develop and manage their personal brands.
The salary of a sports agent within a larger agency can also be influenced by a base salary or draw, though the majority of their compensation still comes from commission.
Factors Beyond Commission: The Full Picture of a Baseball Agent’s Income
While commission is the primary driver, other elements contribute to the overall financial success of a baseball agent.
Understanding the Role of Endorsements
Endorsement deals are often the icing on the cake for both players and their agents. A successful agent acts as a brand strategist for their clients, identifying opportunities that align with the player’s personality, marketability, and public image. These deals can range from national advertising campaigns for major brands to smaller, localized promotions. The commission for baseball agents on these deals can be higher than contract commissions, making them highly sought after.
The Impact of Player Development and Longevity
An agent’s ability to help a player develop their career, maintain longevity in the league, and even transition into post-playing opportunities (like coaching, broadcasting, or business ventures) indirectly impacts their earning potential. A long, successful career for a client means more contract renewals and more years of earning potential, benefiting the agent through sustained MLB agent earnings.
The Competitive Landscape of Sports Representation
The world of baseball representation is highly competitive. Agents must constantly prove their value to attract and retain clients. This involves not only strong negotiation skills but also excellent communication, relationship building, and a deep understanding of the baseball industry. The baseball agent salary reflects this intense competition and the specialized skills required.
Table: Potential Earnings Based on Client Tier
| Client Tier | Average Contract Value (MLB) | Agent Commission (5%) | Potential Endorsement Value (Annual) | Agent Commission on Endorsements (15%) | Total Annual Earnings (Estimate) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minor League | $50,000 – $500,000 (Signing) | $2,500 – $25,000 | Minimal | Minimal | $20,000 – $75,000 (highly variable) |
| Role Player | $1 million – $5 million | $50,000 – $250,000 | $50,000 – $200,000 | $7,500 – $30,000 | $57,500 – $280,000 |
| Solid Starter | $5 million – $15 million | $250,000 – $750,000 | $200,000 – $1 million | $30,000 – $150,000 | $280,000 – $900,000 |
| All-Star | $15 million – $30 million | $750,000 – $1.5 million | $1 million – $5 million | $150,000 – $750,000 | $900,000 – $2.25 million |
| Superstar | $30 million+ | $1.5 million+ | $5 million+ | $750,000+ | $2.25 million – $10 million+ |
Note: These figures are estimates and can vary significantly based on individual circumstances, negotiation outcomes, and market conditions. The baseball agent salary is not a fixed number but a reflection of these variables.
The Journey to Becoming a Successful Baseball Agent
The path to becoming a highly compensated baseball agent is not easy. It requires dedication, a strong understanding of the game, excellent interpersonal skills, and often, a legal or business background.
Essential Skills for Agents
- Negotiation Expertise: The ability to negotiate effectively is non-negotiable.
- Legal Acumen: A grasp of contract law and labor agreements is crucial for contract negotiation commission and player protection.
- Marketing and Sales: Selling a player’s brand to sponsors requires strong marketing skills.
- Networking: Building and maintaining relationships within baseball and corporate circles is vital.
- Financial Literacy: Advising clients on financial matters, even indirectly, is important.
- Communication: Clear, concise, and persuasive communication is key in all aspects of the job.
Building a Client Base
Starting out, agents often represent players they knew from college, high school, or other connections. Gradually building a reputation through successful representation of these initial clients is how they attract more sought-after players. The initial baseball player representation fees might be modest, but they pave the way for larger opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the typical commission rate for baseball agents on player contracts?
A1: The standard commission rate for commission for baseball agents on player contracts is 5% of the total contract value.
Q2: Can baseball agents earn money from endorsement deals?
A2: Yes, baseball agents typically earn commission on endorsement deals, usually ranging from 10% to 20% of the deal’s value. This is a significant part of their overall sports agent income.
Q3: How do agents get paid from a player’s contract?
A3: Agents get paid as the player receives their salary installments. The commission is typically deducted directly from the player’s paychecks by the team and then transferred to the agent. This is how how agents get paid.
Q4: Is there a base salary for baseball agents?
A4: While some agents in larger agencies might receive a small base salary or draw, the vast majority of their income comes from commission for baseball agents. For most, the baseball agent salary is entirely commission-based.
Q5: How much can a top baseball agent realistically earn in a year?
A5: Top baseball agents, representing superstar players with multi-million dollar contracts and lucrative endorsement deals, can earn anywhere from $5 million to over $10 million annually, sometimes even more, contributing to substantial MLB agent earnings.
Q6: What is the average salary for a sports agent in baseball?
A6: There isn’t a definitive average salary for sports agent in baseball due to the commission structure. However, the potential earnings vary dramatically, from tens of thousands for rookie agents to millions for established ones. The overall sports agency revenue is a good indicator of the industry’s financial health.
Q7: What percentage does a baseball agent take from a signing bonus?
A7: The commission rate on signing bonuses is the same as for annual salaries, typically 5%. This contributes to the contract negotiation commission.
Q8: Do agents get paid if a player gets injured and can’t play?
A8: If a player is under contract and receives their salary (perhaps through an injury clause), the agent still earns their commission. However, if the player is released or the contract is terminated due to injury, the agent’s future commission from that player would cease.
Q9: How does the salary of a sports agent compare to other sports?
A9: The salary of a sports agent can vary significantly by sport. Baseball, with its long and lucrative contracts, offers high earning potential, often comparable to or exceeding top agents in sports like football or basketball, depending on the specific client base and deal values.
Q10: What are the main expenses for a baseball agent?
A10: Expenses for baseball agents can include travel to games and client meetings, marketing and promotional materials, legal fees, office overhead (if not working for a large agency), and salaries for any support staff. These expenses are factored into their overall profitability from their sports agency revenue.
